In statistics, a process that consists of prolonging a
statistical series by introducing a new term that obeys the rule of the series to the sequence of given terms.
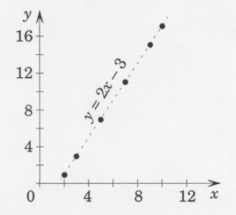
Example
We represented the sequence of statistical data in the table below:
| x |
2 |
3 |
5 |
7 |
9 |
| y |
1 |
3 |
7 |
11 |
15 |
We determine that the relation that best describes this sequence is “y = 2
x − 3.”
By extrapolation, we can determine that, if
x = 30, then
y = 57.